Why and Where GFCI Outlets Are Required: A Safety Guide for Homeowners and Builders
Electricity powers our modern lives, but it also presents serious hazards—especially in areas where water is present. That’s why GFCI (Ground Fault Circuit Interrupter) outlets are not only recommended but required by electrical code in specific locations. These specialized outlets are designed to protect people from electrical shock and help prevent fires caused by ground faults.
What Is a GFCI Outlet?
A GFCI outlet is a safety device that monitors the flow of electricity in a circuit. If it detects an imbalance—such as when current is leaking through a person to the ground—it shuts off power within milliseconds. This quick action can prevent serious injury or even death due to electric shock.
Why GFCI Outlets Are Important
-
Shock Protection: They are the first line of defense in preventing electrical shock in areas where moisture increases the risk.
-
Code Compliance: The National Electrical Code (NEC) mandates GFCI protection in certain areas of residential, commercial, and industrial properties.
-
Fire Prevention: By detecting ground faults early, GFCIs reduce the chance of electrical fires.
-
Property Safety: They protect equipment and appliances from electrical surges caused by faults.
Where GFCI Outlets Are Required (Per NEC Guidelines)
According to the 2023 National Electrical Code, GFCI outlets must be installed in the following areas:
1. Bathrooms
-
Every outlet in a bathroom must be GFCI protected due to the high presence of moisture.
2. Kitchens
-
All outlets serving countertop surfaces require GFCI protection. This includes islands and peninsulas.
3. Garages and Accessory Buildings
-
Outlets in garages and detached buildings with floors at or below grade level must have GFCI protection.
4. Outdoor Areas
-
All outdoor receptacles, including those for landscape lighting or holiday decorations, must be GFCI protected.
5. Basements and Crawlspaces
-
Unfinished basements and all crawlspaces must have GFCI outlets to reduce shock risk in damp or confined environments.
6. Laundry and Utility Rooms
-
Outlets within 6 feet of a sink or appliance like a washing machine or water heater need GFCI protection.
7. Pools, Spas, and Hot Tubs
-
Any receptacle within 20 feet of the water’s edge must be GFCI protected.
8. Boathouses and Docks
-
All receptacles in boathouses and on floating docks must have GFCI protection to mitigate shock hazards around water.
9. Dishwashers and Garbage Disposals
-
GFCI protection is required even for hardwired dishwashers and disposals due to their potential contact with water.
Final Thoughts
GFCI outlets are a simple, affordable way to increase electrical safety in any structure. Whether you’re a homeowner doing renovations or a builder designing new homes, knowing where and why these outlets are required ensures you stay code-compliant and reduce risk. Proper installation not only protects lives but also adds long-term value and safety to the property.

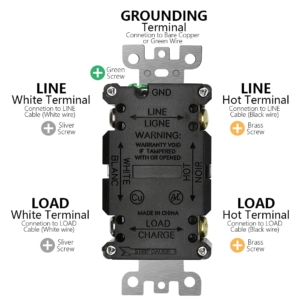



 Our Construction company is Servicing Southeast Michigan, Detroit and the Tri-County area Wyane, Oakland and Macomb;
Our Construction company is Servicing Southeast Michigan, Detroit and the Tri-County area Wyane, Oakland and Macomb;